All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit Know ALL.
The all Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the all Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The all and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The ALL Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Amgen, Autolus, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer and supported through an educational grant from the Hippocrate Conference Institute, an association of the Servier Group. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View ALL content recommended for you
Efficacy and safety of sequential CD19 and CD22 CAR T-cell therapy for childhood R/R B-ALL
Question 1 / 1
Of the 62 patients who received the target dose of CD19 and CD22-directed CAR T-cell therapy, what percentage achieved measurable residual disease-negative complete remission (CR) or complete remission with incomplete hematological recovery (CRi)?
A
a) 72%
B
b) 87%
C
c) 91%
D
d) 97%
CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies have demonstrated promising outcomes in patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) B-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia (B-ALL); however, 30%–50% of this patient population experience relapse. Bispecific CAR approaches that simultaneously target CD19 and CD22 are an effective treatment option and have successfully reduced antigen-escape-based relapse rates.
Below, we summarize the results of a phase II trial published by Pan et al. in Lancet Oncology, highlighting the safety and efficacy of sequential CD19-directed and CD22-directed CAR T-cell treatments in patients with R/R B-ALL.
Study design1
This was a single center, single-arm, phase II trial that included:
- Patients aged 1–18 years with R/R B-ALL with CD19 and CD22 positivity >95%
- An Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status of 0–2.
Before each CAR T-cell infusion, patients received fludarabine (30 mg/m² per day) and cyclophosphamide (250 mg/m² per day) intravenously on Days −5, −4, and −3 to reach lymphodepletion.
Patients were infused with fresh CD19-directed CAR T cells intravenously, followed by CD22-directed CAR T cells immediately after manufacture, and once measurable residual disease (MRD)-negative complete remission (CR) or complete remission with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi) was reached, and all adverse events (AEs) were Grade 2 or better (except hematologic AEs).
Treatment cycles were defined as:
- Cycle 1 = the time from CD19-directed CAR T-cell infusion to before the second lymphodepletion.
- Cycle 2 = the time from CD22-directed CAR T-cell infusion to 30 days thereafter.
Endpoints
The primary endpoint was objective response rate, including MRD-negative CR and CRi 3 months after the infusion.
The secondary endpoints included:
- Event-free survival, defined as the time from first infusion to earliest relapse, treatment failure, or death from any cause
- Overall survival, defined as the time from first infusion to death from any cause
- Duration of remission, defined as the time from initial CR or CRi to recurrence or death from ALL.
- Disease-free survival, defined as the time from first infusion to earliest relapse or death from ALL
- Adverse events
- Pharmacokinetics, which included the expansion and persistence of CD19 and CD22 CAR T cells in the peripheral blood, and if needed in the cerebrospinal fluid and bone marrow
- B-cell count
Results
Overall, 81 patients were enrolled in this study. Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Patient characteristics*
|
CNS, central nervous system; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; IQR, interquartile range. |
|
|
Characteristic, % (unless otherwise stated) |
All treated patients |
|---|---|
|
Median age, years (IQR) |
8 (6–10) |
|
Sex |
|
|
Female |
38 |
|
Male |
62 |
|
Race |
|
|
Asian |
100 |
|
Ethnicity |
|
|
Chinese Han |
91 |
|
Chinese ethnic minorities† |
9 |
|
Extramedullary disease |
|
|
Any |
19 |
|
Diffuse‡ |
1 |
|
Testicular |
6 |
|
CNS |
9 |
|
Other locations§ |
2 |
|
ECOG performance |
|
|
0–1 |
98 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
Relapsed or refractory subgroup |
|
|
Relapsed after last therapy |
68 |
|
Refractory to last therapy |
32 |
|
Number of previous lines of therapy |
|
|
1 |
38 |
|
2 |
41 |
|
≥3 |
21 |
|
Previous HSCT |
|
|
Yes |
12 |
|
No |
88 |
|
Baseline marrow blasts by morphology‖ |
|
|
<5% |
42 |
|
≥5% to <50% |
38 |
|
≥50% |
20 |
|
Genetic features¶ |
|
|
Favorable |
22 |
|
Unfavorable |
11 |
At a median follow-up of 17.7 months, a total of 79 patients received sequential CAR T-cell therapy; two patients discontinued the study after CD19-directed CAR T-cell infusion; therefore, did not receive the CD22-directed CAR T-cells.
Overall, 81 patients received the target dose of CD19-directed CAR T cells (median 2.7 × 10⁶ cells per kg [interquartile range, 1.1 × 10⁶ to 3.7 × 10⁶]) and CD22-directed CAR T cells (2.2 × 10⁶ cells per kg [interquartile range, 1.1 × 10⁶ to 3.8 × 10⁶]). Two patients received the target dose of CD19-directed but not of CD22-directed CAR T cells.
Response
- Of the 81 patients who received at least the first infusion, 98% had MRD-negative CR or CRi 3 months after infusion (Figure 1B).
- Of the 79 patients who had remission at 3 months, 63 patients remained in remission and alive, and one remained in remission until death from graft-versus-host-disease post hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
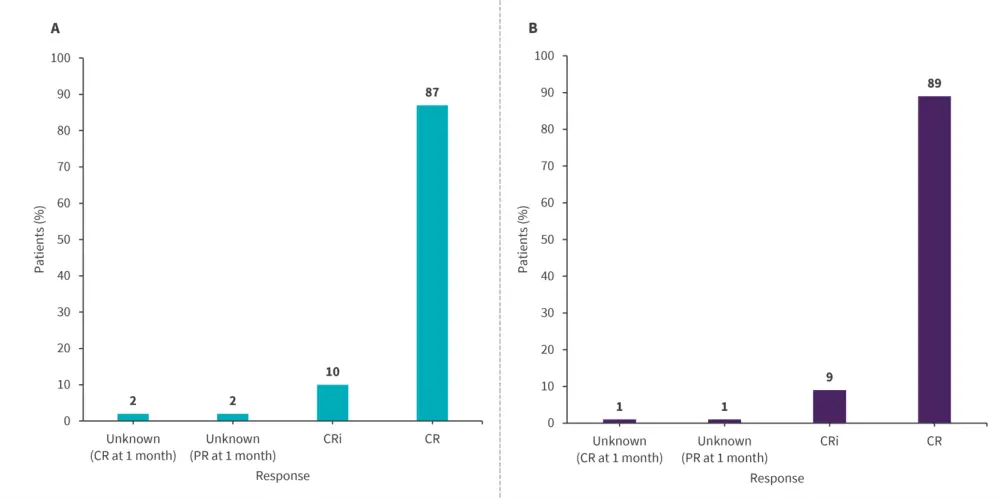
CR, complete remission; CRi, CR with incomplete hematological recovery; PR, partial remission.
*Adapted from Pan, et al.1
Survival
- The 18 month-event free survival for patients who received the target dose was 79%.; this rate was similar for all treated patients.
- The 18-month overall survival was 96% for all patients.
- The 18-month disease-free survival and duration of remission with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation censoring for patients who received the target doses and for all treated patients were 80% and 79%, respectively.
Safety
All patients experienced AEs (Table 2), none required dose reductions or discontinuation due to toxicity, and no treatment-related deaths occurred. Severe cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity events occurred less frequently in Cycle 2 than in Cycle 1.
Table 2. Adverse events
|
CRS, cytokine release syndrome; ICANS, immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome. |
||||||
|
Adverse events, n (%) |
Cycle 1 (N = 81) |
Cycle 2 (N = 79) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grade 1–2 |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 |
Grade 1–2 |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 |
|
|
Any† |
30% |
40% |
31% |
32% |
43% |
25% |
|
CRS‡ |
74% |
15% |
1% |
68% |
3% |
3% |
|
ICANS§ |
23% |
4% |
1% |
16% |
1% |
0 |
|
Infection† |
5% |
4% |
0 |
5% |
5% |
0 |
|
Hematologic† |
41% |
30% |
30% |
38% |
38% |
24% |
Conclusion
In this phase II trial, sequential CD19-directed and CD22-directed CAR T-cell therapy induced deep and sustainable responses and demonstrated an acceptable toxicity profile in childhood R/R B-cell ALL. A further randomized controlled trial is being planned due to these findings.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content

