All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit Know ALL.
The all Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the all Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The all and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The ALL Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Amgen, Autolus, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer and supported through an educational grant from the Hippocrate Conference Institute, an association of the Servier Group. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View ALL content recommended for you
Impact of obesity on asparaginase dosing and outcomes in adult patients with ALL
The use of asparaginase is challenging in older and/or obese adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) due to the higher risk of asparaginase-related toxicities; this has resulted in its selective use or avoidance in these patient populations.1
Here, we summarize a review published by Cassaday et al.1 in Best Practice & Research Clinical Haematology on the impact of obesity on outcomes with asparaginase-containing regimens in patients with ALL, as well as recommendations for the use of asparaginase.
Key findings
Impact of obesity on outcomes
Key data from selected studies on the impact of obesity on outcomes and risks with asparaginase-containing regimens for children, adolescents, and adults with ALL are summarized in Figure 1; increasing age can also increase these risks.
Figure 1. Key findings on the impact of obesity with asparaginase-containing regimens*
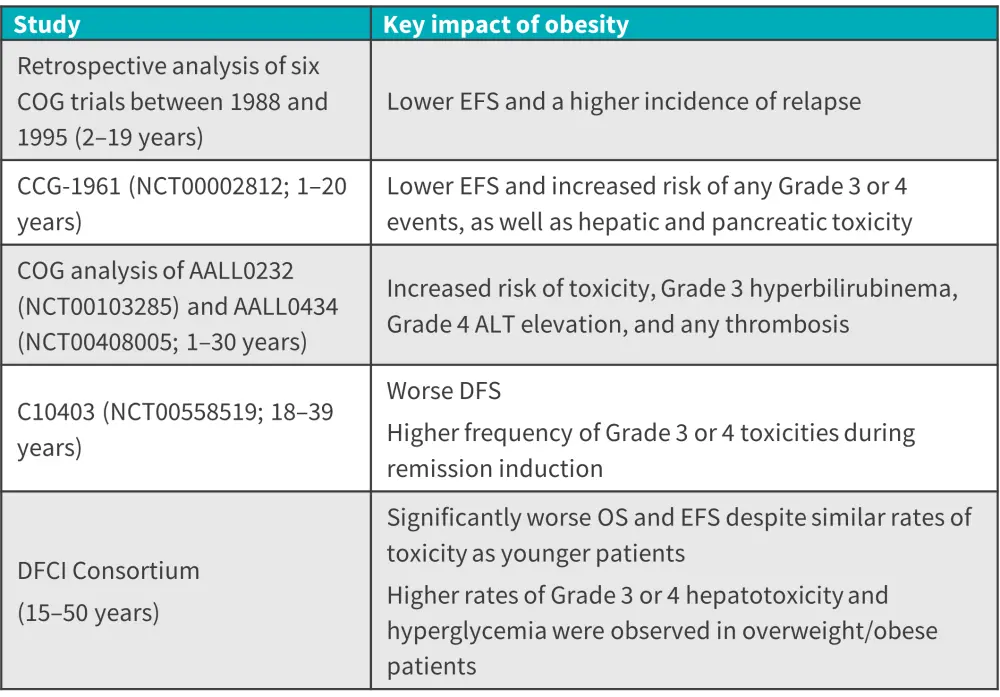
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; BSA, body surface area; BMI, body mass index; COG, Children’s Oncology Group; DFCI, Dana Farber Cancer Institute; DFS, disease-free survival; EFS, event-free survival; OS, overall survival.
*Adapted from Cassaday.1
Strategies to optimize the use of asparaginase
- Use of shorter-acting asparaginase products
- Cap the dose of pegaspargase
- Switch to a non-asparaginase-containing regimen, such as hyperCVAD
Clinical approach to asparaginase-containing regimens in adult ALL
A clinical approach to asparaginase-containing regimens in adult ALL is presented in Figure 2.
- Pegaspargase is routinely capped at a dose of 3,750 units to reduce the risk of toxicities
- A lower dose of pegaspargase (e.g., 1,000 units/m2) or switching to another regimen, such as hyperCVAD, should be considered
- Weight loss should be encouraged to reduce the risk of complications
Figure 2. Clinical approach to asparaginase-containing regimens in adult ALL*
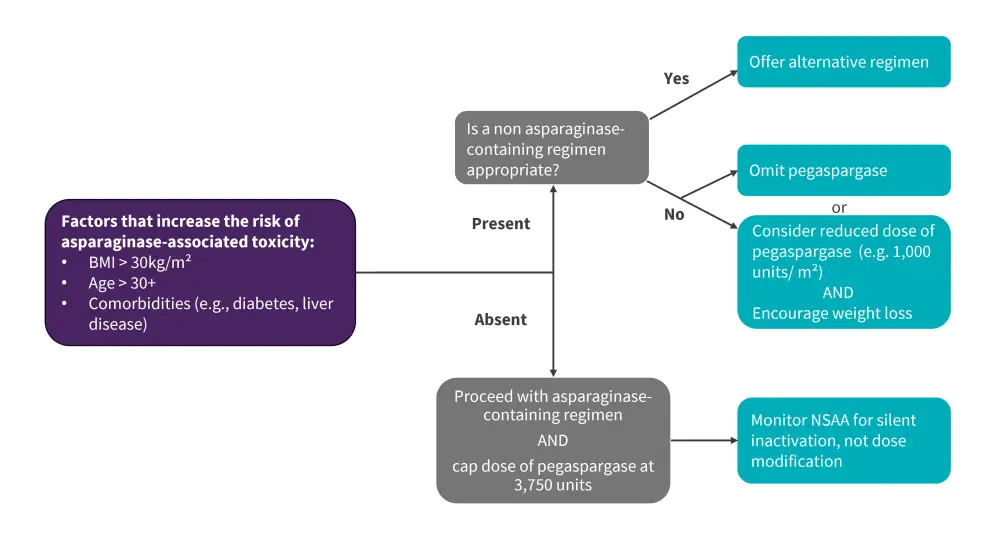
ALL, acute lymphoblastic leukemia; BMI, body mass index; NSAA, nadir serum asparaginase activity assessment.
*Adapted from Cassaday.1
| Key learnings and future directions |
|
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content




